
If not treated, eventually, compartment syndrome may require amputation of the affected limb.

Some fractures may lead to serious complications including a condition known as compartment syndrome. Complications An old fracture with nonunion of the fracture fragments Involuntary muscle spasms trying to hold bone fragments in place.ĭamage to adjacent structures such as nerves, muscles or blood vessels, spinal cord, and nerve roots (for spine fractures), or cranial contents (for skull fractures) may cause other specific signs and symptoms.Edema and hematoma of nearby soft tissues caused by ruptured bone marrow evokes pressure pain.Breaking in the continuity of the periosteum, with or without similar discontinuity in endosteum, as both contain multiple pain receptors.Signs and symptoms Īlthough bone tissue contains no pain receptors, a bone fracture is painful for several reasons: A bone fracture may be the result of high force impact or stress, or a minimal trauma injury as a result of certain medical conditions that weaken the bones, such as osteoporosis, osteopenia, bone cancer, or osteogenesis imperfecta, where the fracture is then properly termed a pathologic fracture.
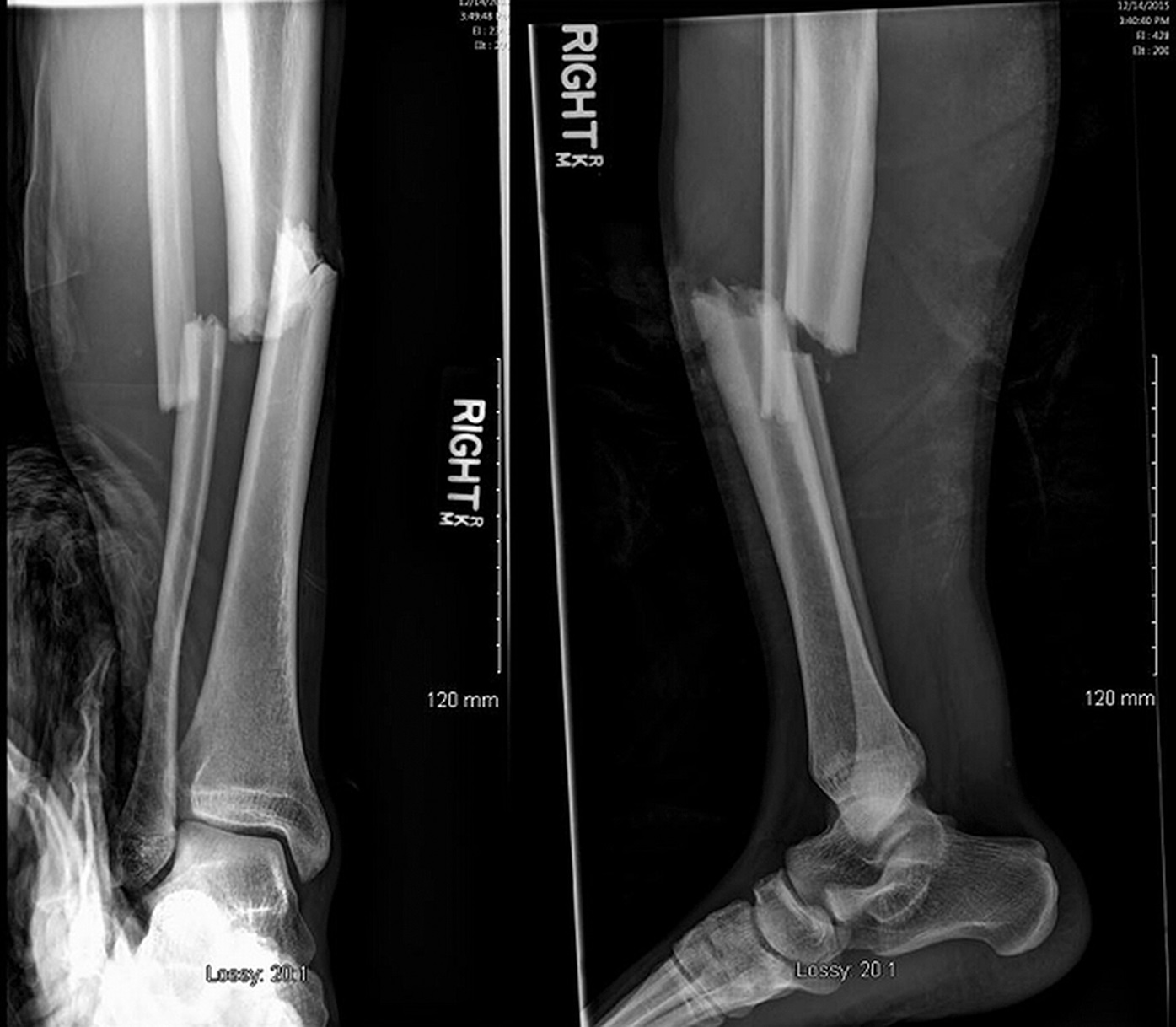
In more severe cases, the bone may be broken into several fragments, known as a comminuted fracture. Internal and external views of an arm with a compound fracture, both before and after surgeryĪ bone fracture (abbreviated FRX or Fx, F x, or #) is a medical condition in which there is a partial or complete break in the continuity of any bone in the body.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
